This study focuses on the assessment of hemodynamic impact of intracranial atherosclerotic disease (ICAD) using 4D flow MRI. ICAD is one of the main causes of ischemic stroke worldwide and is associated with a high risk of stroke recurrence in patients potentially due to hemodynamic failure. Therefore, the evaluation of hemodynamic influences of the lesion on the cerebral blood flow distribution and blood flow in stenotic vessels may be useful for ICAD characterization and risk stratification. Here, we use dual-venc 4D flow MRI for in-vivo measurement of time-resolved and 3D velocity of blood in major cerebral arteries.
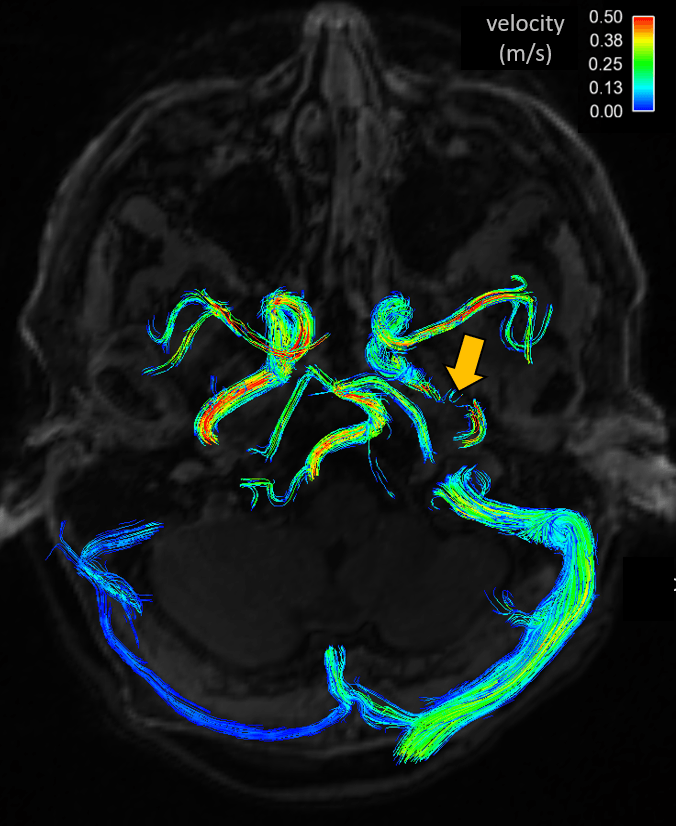
Systolic 3D streamlines demonstrating the blood flow field colored by velocity magnitude in an ICAD patient with stenosis of the right ICA (the location of the lesion is shown by arrow)
We use the Bernoulli equation to estimate pressure drop at the atherosclerotic stenosis from MRI, which demonstrated promising results for assessing the lesion.
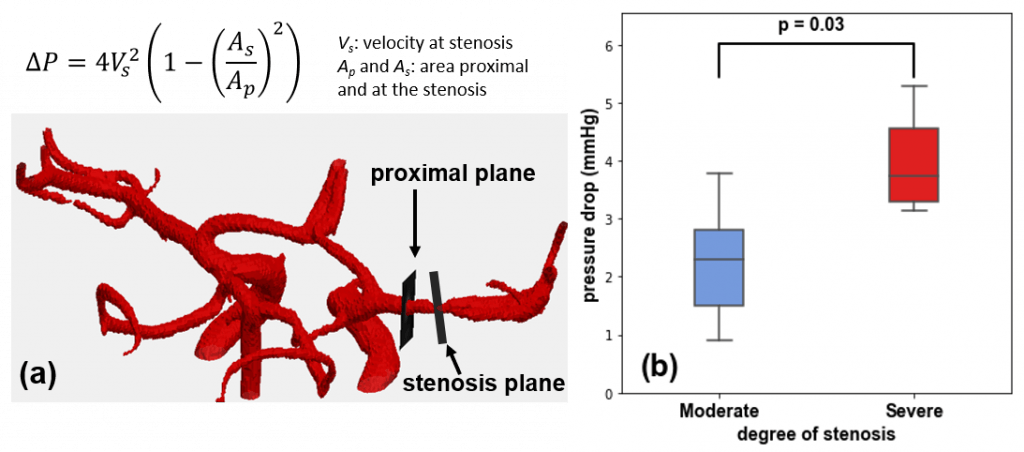
(a) Bernoulli equation and the locations for quantification of parameters used for pressure drop calculation, (b) pressure drop for ICAD patients with moderate and severe stenosis
In addition, we investigate cerebral blood flow distribution in the Circle of Willis in both healthy volunteers and ICAD patients to evaluate potential changes due to the disease. It was found that intracranial atherosclerotic lesion not only altered distal arterial flow but also affected blood flow in other intracranial arterial branches.
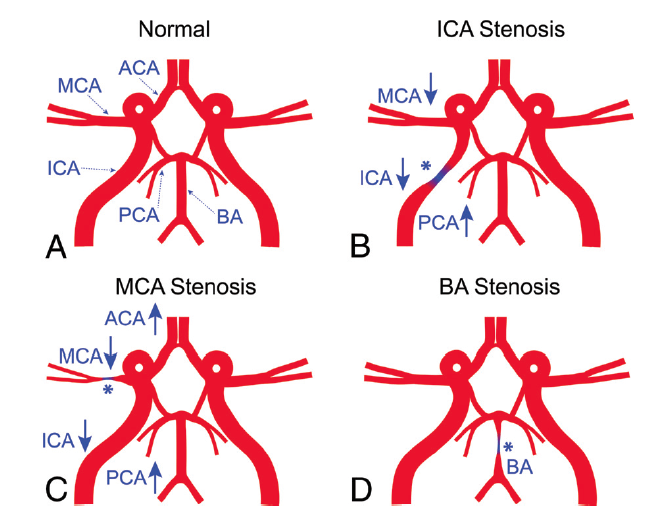
Schematic diagram of the Circle of Willis (A, normal; B, ICA stenosis; C, MCA stenosis; and D, BA stenosis) the asterisk represents the location of the stenosis. The up arrow and down arrow indicate a relative increase or decrease of flow in the local vessel compared with the contralateral counterpart in patients with ICAD.
Future longitudinal studies can examine the use of our findings for the assessment of recurrent stroke risk in patients with ICAD.
Funding: AHA Postdoctoral Grant 18POST33990451
Publications and Abstracts:
-
Vali A, Aristova M, Vakil P, Abdalla R, Prabhakaran S, Markl M, Ansari SA, Schnell S. Magn Reson Med. 2019 Aug;82(2):749-762. DOI: 10.1002/mrm.27747. Epub 2019 Mar 28.
- Alireza Vali, Maria Aristova, Sameer A. Ansari, Ayesha Muzaffar, Shyam Prabhakaran, Michael Markl, and Susanne Schnell, Hemodynamic biomarkers to assess disease severity in patients with intracranial atherosclerotic disease using dual-venc 4D flow MRI, International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine (ISMRM) 2018, Paris, France
- Alireza Vali, Maria Aristova, Sameer A. Ansari, Ayesha Muzaffar, Shyam Prabhakaran, Michael Markl, Susanne Schnell, Feasibility of automated analysis of dual-venc 4D flow MRI to assess hemodynamics in patients with intracranial atherosclerotic disease, the American Heart Association, International Stroke Conference (ISC) 2018, Los Angeles, CA, USA
- Wu C, Schnell S, Vakil P, Honarmand AR, Ansari SA, Carr J, Markl M and Prabhakaran S. In Vivo Assessment of the Impact of Regional Intracranial Atherosclerotic Lesions on Brain Arterial 3D Hemodynamics. AJNR American journal of neuroradiology. 2017;38:515-522
